Building dna gizmo answers activity b – Embark on a journey of discovery with the captivating Building DNA Gizmo: Answers Activity B. This activity delves into the intricate world of DNA, unveiling its structure, function, and the significance of analyzing its sequences to identify mutations and variations.
Join us as we unravel the secrets of DNA, exploring its role in biological processes and its applications in real-world scenarios.
Through hands-on exploration using the DNA Gizmo, you will gain a deeper understanding of DNA’s double-helix structure, its nucleotide components, and its function in storing and transmitting genetic information. Learn how to construct and manipulate DNA sequences, gaining valuable insights into the processes of protein synthesis and other biological functions.
DNA Structure and Function

DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the genetic material that carries the instructions for an organism’s development and characteristics. It is found in the nucleus of cells and is made up of four different types of nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
The nucleotides are arranged in a specific order that determines the genetic code. The code is read by cells to produce proteins, which are essential for the structure and function of the organism.
Double-Helix Structure
DNA has a double-helix structure, which means that it is made up of two strands that are twisted around each other. The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nucleotides. The shape of the double helix allows DNA to be very compact and to store a large amount of information in a small space.
Role in Storing and Transmitting Genetic Information
DNA is the genetic material that carries the instructions for an organism’s development and characteristics. The code is read by cells to produce proteins, which are essential for the structure and function of the organism.
When a cell divides, the DNA is copied so that each new cell has a complete set of genetic instructions.
Examples of DNA Use in Biological Processes
- Protein synthesis: DNA is used to produce proteins, which are essential for the structure and function of cells.
- Cell division: DNA is copied before a cell divides so that each new cell has a complete set of genetic instructions.
- Genetic inheritance: DNA is passed from parents to offspring, which allows for the transmission of genetic traits.
Building a DNA Gizmo

The DNA Gizmo is an interactive simulation that allows students to build and manipulate DNA sequences. It is a valuable tool for teaching students about the structure and function of DNA, as well as the processes of DNA replication and transcription.
Components of the DNA Gizmo
The DNA Gizmo consists of a number of components, including:
- A DNA strand builder: This tool allows students to build DNA sequences by adding and removing nucleotides.
- A DNA sequence viewer: This tool allows students to view the DNA sequence they have built, as well as the corresponding mRNA and protein sequences.
- A DNA replication simulator: This tool allows students to simulate the process of DNA replication.
- A DNA transcription simulator: This tool allows students to simulate the process of DNA transcription.
Using the DNA Gizmo, Building dna gizmo answers activity b
To use the DNA Gizmo, students first need to select the type of DNA sequence they want to build. They can choose from a variety of templates, including a blank strand, a gene, or a virus.
Once they have selected a template, students can begin building their DNA sequence by adding and removing nucleotides. They can also use the DNA strand builder to create custom DNA sequences.
Once students have built their DNA sequence, they can use the DNA sequence viewer to view the sequence, as well as the corresponding mRNA and protein sequences.
Students can also use the DNA replication simulator to simulate the process of DNA replication. This simulator allows students to see how DNA is copied during cell division.
Finally, students can use the DNA transcription simulator to simulate the process of DNA transcription. This simulator allows students to see how DNA is used to create mRNA and protein.
Tips for Students
Here are a few tips for students using the DNA Gizmo:
- Start by building a simple DNA sequence. This will help you get the hang of using the Gizmo.
- Use the DNA sequence viewer to check your work. This will help you make sure that your DNA sequence is correct.
- Use the DNA replication simulator to see how DNA is copied during cell division.
- Use the DNA transcription simulator to see how DNA is used to create mRNA and protein.
Activity B: Analyzing DNA Sequences: Building Dna Gizmo Answers Activity B
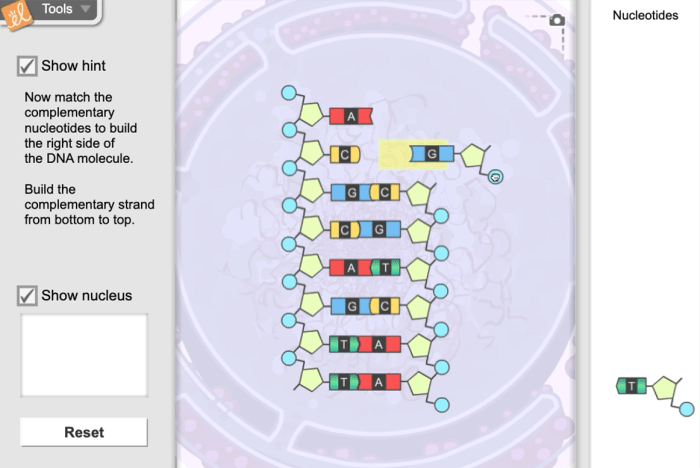
Activity B of the Building DNA Gizmo aims to provide students with an interactive platform to analyze DNA sequences and identify mutations and variations.
By manipulating the DNA sequence in the Gizmo, students can explore different types of mutations, such as insertions, deletions, and substitutions. They can also investigate variations in DNA sequences, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs).
Applications of DNA Sequence Analysis
Analyzing DNA sequences has numerous applications in real-world scenarios:
- Medical diagnostics:DNA sequence analysis can identify genetic mutations associated with diseases, allowing for personalized medicine and early detection of health risks.
- Forensic science:DNA profiling techniques, which analyze variations in DNA sequences, are used to identify individuals and establish genetic relationships in criminal investigations and paternity testing.
DNA Gizmo Table

The DNA Gizmo Table presents a comprehensive overview of various mutation types, their descriptions, and illustrative examples. This table serves as a valuable resource for understanding the diverse range of mutations and variations that can occur within DNA sequences.
Mutation Types
- Substitution:Replaces one nucleotide with another, resulting in a change in the genetic code. Example: ATG → ACT (changes codon from methionine to threonine)
- Insertion:Adds an extra nucleotide into the sequence, causing a shift in the reading frame. Example: ATG → ATGT (inserts thymine, causing a frameshift mutation)
- Deletion:Removes a nucleotide from the sequence, also causing a frameshift mutation. Example: ATG → AT (deletes guanine, causing a frameshift mutation)
- Inversion:Reverses the order of a segment of DNA. Example: ATG → GTA (reverses the order of the nucleotides)
- Translocation:Moves a segment of DNA from one location to another. Example: ATG → GCAT (moves the ATG segment to the end of the sequence)
By utilizing the DNA Gizmo, researchers can identify and analyze these different types of mutations and variations within DNA sequences. This analysis provides insights into the genetic basis of diseases, the evolution of species, and the mechanisms underlying DNA repair and replication.
Key Questions Answered
What is the purpose of the DNA Gizmo Activity B?
The purpose of Activity B is to analyze DNA sequences to identify mutations and variations, providing insights into the genetic makeup of organisms.
What types of mutations and variations can be identified using the Gizmo?
The Gizmo allows for the identification of various types of mutations and variations, including substitutions, insertions, deletions, and inversions.
How can analyzing DNA sequences be used in real-world applications?
Analyzing DNA sequences finds applications in medical diagnostics, forensic science, and genetic research, aiding in disease diagnosis, criminal investigations, and understanding genetic disorders.