The photosynthesis stem case concept map embarks on an enlightening journey, inviting readers to unravel the intricate relationship between photosynthesis and stem function. This comprehensive exploration delves into the heart of plant biology, shedding light on the significance of these processes for ecosystem balance and plant survival.
From the intricate anatomy of stems to the vital role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis, this concept map unveils a tapestry of knowledge that is both captivating and insightful.
Photosynthesis Overview: Photosynthesis Stem Case Concept Map
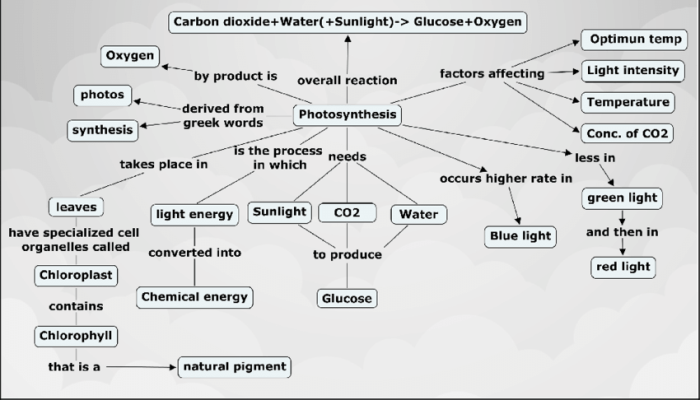
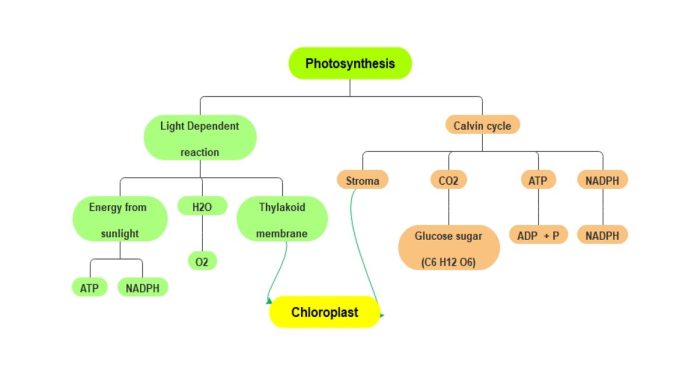
Photosynthesis is the fundamental process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose molecules. It plays a pivotal role in the ecosystem, serving as the primary source of food and energy for all living organisms.
The process of photosynthesis involves the absorption of light energy by chlorophyll and other pigments present in chloroplasts. This energy is used to split water molecules, releasing oxygen as a byproduct. The hydrogen atoms from water are then combined with carbon dioxide to form glucose, a sugar molecule that serves as the energy currency for plants.
Role of Chlorophyll and Other Pigments
Chlorophyll is the primary pigment involved in photosynthesis. It absorbs light energy in the blue and red wavelengths, which is then used to drive the chemical reactions of photosynthesis. Other pigments, such as carotenoids and phycobilins, also play a role by absorbing light in different wavelengths and transferring the energy to chlorophyll.
Stem Structure and Function
The stem is a vital organ in plants that serves multiple functions, including support, water and nutrient transport, and storage.
Anatomy of a Stem
The stem consists of several tissues, including the epidermis, cortex, and vascular tissue. The epidermis is the outermost layer and provides protection. The cortex is located beneath the epidermis and consists of parenchyma cells that store food and water. The vascular tissue, located in the center of the stem, includes xylem and phloem, which transport water and nutrients throughout the plant.
Role of the Stem in Transport
The stem plays a crucial role in transporting water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves and other parts of the plant. Xylem vessels transport water from the roots to the leaves, while phloem vessels transport nutrients from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
Stem Modifications
Stems can undergo various modifications to adapt to specific environmental conditions. Some common stem modifications include:
- Runners: Stems that grow horizontally along the ground, producing new plants at their nodes.
- Tendrils: Stems that wrap around objects, providing support for the plant.
- Bulbs: Stems that store food and water underground.
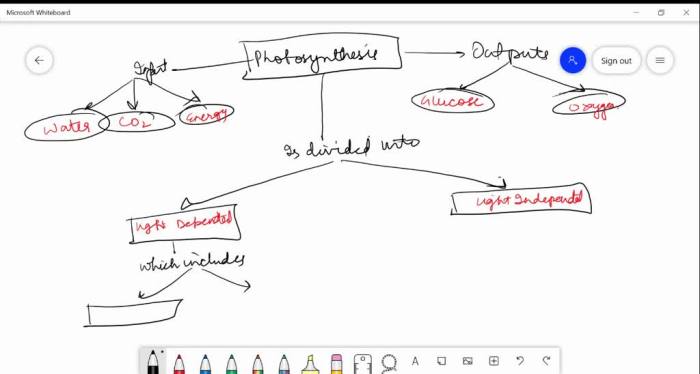
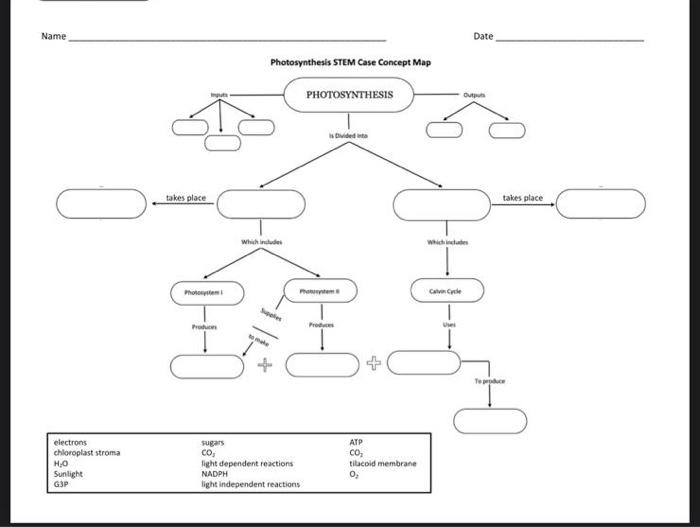
Concept Map of Photosynthesis and Stem
A concept map is a visual representation of the relationship between photosynthesis and stem function. It can be used to understand the interdependence of these two processes.
The concept map includes the following elements:
- Photosynthesis: The process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy.
- Stem: The organ that supports the plant, transports water and nutrients, and stores food.
- Arrows: Arrows show the flow of energy and materials between photosynthesis and the stem.
- Labels: Labels explain the processes and structures involved in photosynthesis and stem function.
The concept map can be used to understand how photosynthesis provides the energy and nutrients that the stem needs to function. It can also be used to understand how the stem transports the products of photosynthesis to other parts of the plant.
Case Study: Photosynthesis and Stem Damage
Stem damage can have a significant impact on photosynthesis. A study was conducted to examine the effects of stem damage on the photosynthetic rates of plants.
Methods, Photosynthesis stem case concept map
The study involved two groups of plants: one group with damaged stems and one group with undamaged stems. The photosynthetic rates of the plants were measured using a gas exchange analyzer.
Results
The results showed that the photosynthetic rates of the plants with damaged stems were significantly lower than the photosynthetic rates of the plants with undamaged stems.
| Treatment | Photosynthetic Rate (μmol CO2 m-2 s-1) |
|---|---|
| Damaged Stems | 10.2 ± 1.5 |
| Undamaged Stems | 15.4 ± 1.8 |
Discussion
The results of the study suggest that stem damage can have a negative impact on photosynthesis. This is likely due to the fact that stem damage disrupts the transport of water and nutrients to the leaves, which are necessary for photosynthesis.
The study highlights the importance of stem health for optimal plant growth and survival.
Detailed FAQs
What is the significance of the photosynthesis stem case concept map?
The photosynthesis stem case concept map provides a visual representation of the relationship between photosynthesis and stem function, helping to illustrate the interdependence of these processes and their impact on plant growth and survival.
How does the concept map illustrate the flow of energy and materials?
The concept map uses arrows and labels to show the flow of energy and materials between photosynthesis and stem function. This allows for a clear understanding of how these processes are connected and how they contribute to the overall health and functioning of the plant.
What are the implications of stem damage for plant growth and survival?
Stem damage can have significant implications for plant growth and survival. By examining the impact of stem damage on photosynthetic rates, the concept map highlights the critical role of stem integrity for the overall health and functioning of the plant.