A closed rigid tank is filled with water – A closed rigid tank filled with water presents a fascinating subject for exploration in engineering. This analysis delves into the intricate behavior of water confined within an impermeable and rigid container, examining its properties, thermodynamics, and practical applications.
Understanding the behavior of water in closed rigid tanks is crucial for various engineering disciplines, including fluid mechanics, thermodynamics, and structural design. This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the key concepts and principles involved, laying the groundwork for further exploration and practical applications.
Introduction
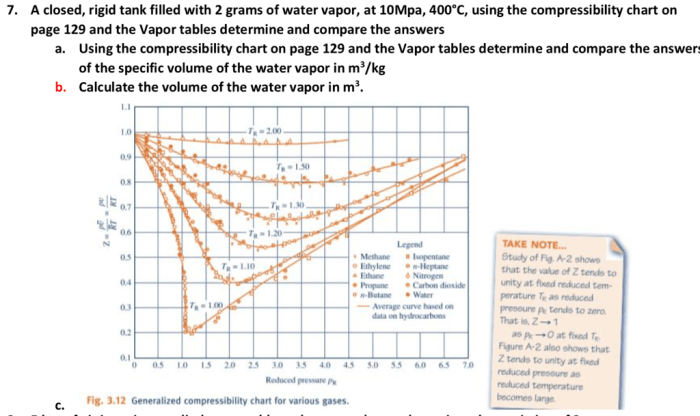
Closed rigid tanks are frequently used in engineering applications to store and contain fluids under various conditions. This analysis aims to investigate the behavior of water contained within a closed rigid tank, examining its physical properties, thermodynamic processes, and the forces acting upon it.
Closed Rigid Tank Characteristics
A closed rigid tank is a container with impermeable and rigid walls, meaning that no mass can enter or leave the tank, and its volume remains constant. The analysis assumes the tank has a specific shape and material properties, which influence its behavior and the forces acting upon it.
Water Properties
Water is an incompressible fluid, meaning its volume remains relatively constant under varying pressure conditions. Its physical and thermodynamic properties, such as density, specific heat, and thermal conductivity, are crucial in understanding its behavior within the tank.
Fluid Statics
Fluid statics principles govern the behavior of water within the tank. Pressure, buoyancy, and hydrostatic forces play significant roles in determining the forces acting on the tank and its contents. These principles can be applied to calculate the pressure distribution, buoyant forces, and the overall forces acting on the system.
Thermodynamics of Water: A Closed Rigid Tank Is Filled With Water

Water undergoes various thermodynamic processes within the closed rigid tank, including heating, cooling, and phase changes. The concepts of internal energy, enthalpy, and entropy are essential in understanding these processes and their impact on the system’s behavior. The relationship between pressure, temperature, and volume is crucial in analyzing the thermodynamic state of water.
Applications and Case Studies
Closed rigid tanks filled with water find applications in various engineering fields, such as power plants, hydraulic systems, and chemical processing. Case studies demonstrate the practical use of the principles discussed in the analysis, showcasing the importance of understanding the behavior of water in these systems.
Popular Questions
What is the significance of closed rigid tanks in engineering applications?
Closed rigid tanks are widely used in engineering systems for storing and transporting fluids under pressure. They play a crucial role in various applications, such as hydraulic systems, boilers, pressure vessels, and thermal energy storage systems.
How does the assumption of water’s incompressibility affect the analysis?
The assumption of water’s incompressibility simplifies the analysis by neglecting changes in water’s volume under pressure. This assumption is valid for most practical applications where the pressure variations are relatively small.
What are the key thermodynamic processes that can occur within a closed rigid tank filled with water?
The primary thermodynamic processes that can occur within a closed rigid tank filled with water are heating, cooling, and phase changes (e.g., evaporation and condensation). These processes involve changes in water’s temperature, pressure, and internal energy.