Extinct language definition AP Human Geography embarks on an enthralling journey into the realm of lost languages, unraveling the complexities of language death and its profound impact on human history and culture.
This exploration delves into the causes and consequences of language extinction, examining the factors that drive languages to the brink of oblivion. It sheds light on the cultural and historical significance of extinct languages, highlighting their role in shaping our understanding of past societies and their influence on present-day place names and cultural practices.
Extinct Language Definition: Extinct Language Definition Ap Human Geography
An extinct language is a language that is no longer spoken or written by any living person. Language death occurs when the last native speaker of a language dies, or when a language is no longer used for communication in any context.
Examples of extinct languages include Latin, Ancient Greek, and Akkadian. These languages died out due to a variety of factors, including conquest, assimilation, and societal changes.
Impact of Extinct Languages on Human Geography
Extinct languages hold significant cultural and historical value. They provide insights into the past societies and cultures that spoke them. The loss of extinct languages can make it difficult to understand the history and traditions of these cultures.
For example, the extinct language of Moche, spoken by the Moche people of Peru, has helped archaeologists to understand the Moche culture and their complex society.
Causes of Language Extinction
The primary causes of language extinction include:
- Assimilation: When a group of people adopts the language of another group, often due to conquest or migration.
- Displacement: When a group of people is forced to move from their homeland, often due to war or persecution, and their language is no longer spoken in their new environment.
- Societal changes: When a society undergoes significant changes, such as industrialization or urbanization, which can lead to the loss of traditional languages.
Other factors that can contribute to language extinction include colonialism, globalization, and technology.
Efforts to Preserve Extinct Languages
There is a growing movement to preserve extinct languages. This is important for cultural and linguistic diversity, as well as for the understanding of past societies and cultures.
Methods used to document and revitalize extinct languages include:
- Transcription: Creating written records of extinct languages from oral traditions or historical documents.
- Reconstruction: Using linguistic methods to recreate extinct languages based on related languages or historical records.
- Revitalization: Teaching extinct languages to new speakers, often in an effort to revive the language as a living language.
Applications of Extinct Language Research
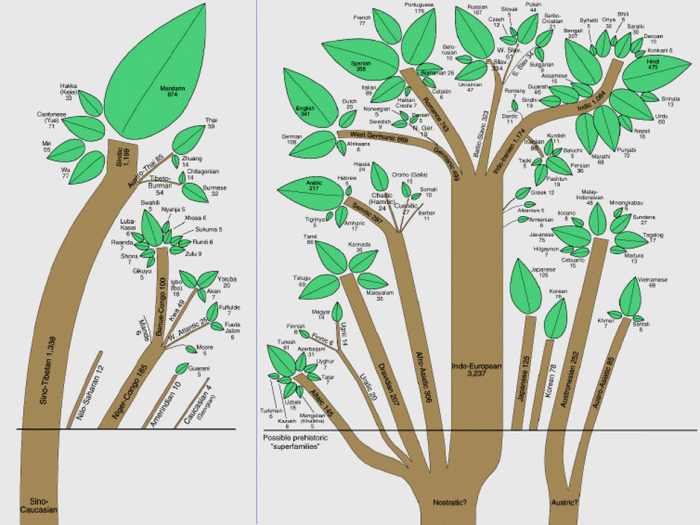
The study of extinct languages contributes to our understanding of language evolution and linguistics. It can also provide insights into the history and culture of past societies.
For example, the study of extinct languages has helped linguists to understand the origins and development of Indo-European languages.
Questions Often Asked
What is the definition of an extinct language?
An extinct language is a language that no longer has any native speakers.
What are the primary causes of language extinction?
Assimilation, displacement, and societal changes are the primary causes of language extinction.
Why is it important to preserve extinct languages?
Preserving extinct languages is important for cultural and linguistic diversity and provides insights into language evolution and human history.