Which statement is correct regarding glargine insulin? This query opens the door to an in-depth examination of this long-acting insulin analog, shedding light on its mechanism of action, clinical applications, advantages, and disadvantages. Prepare to delve into a comprehensive exploration that will empower you with a thorough understanding of glargine insulin’s role in diabetes management.
Glargine insulin, a cornerstone in the treatment of diabetes, stands out for its unique properties. Its extended duration of action, coupled with its favorable safety profile, positions it as a cornerstone therapy for individuals seeking optimal glycemic control.
Glargine Insulin Definition and Mechanism of Action
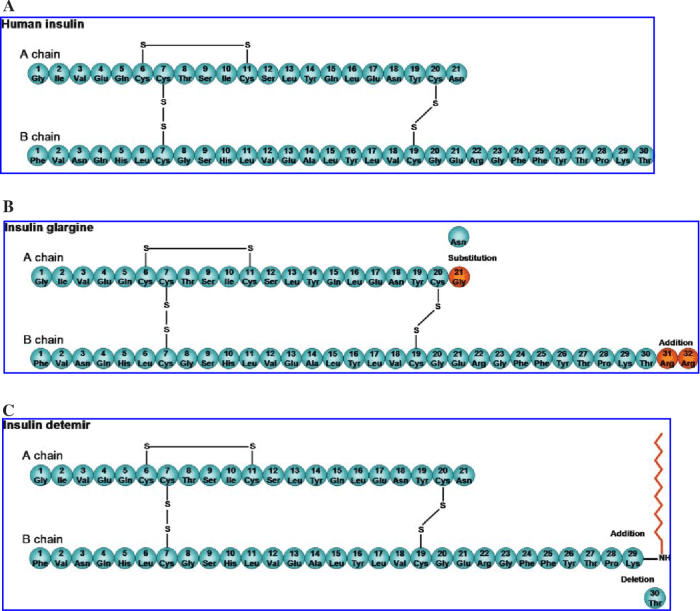
Glargine insulin is a long-acting insulin analog that is used to treat diabetes. It is a recombinant human insulin that has been modified by the addition of two arginine residues to the B chain and one glutamic acid residue to the A chain.
This modification results in a change in the isoelectric point of insulin, which makes it less soluble at neutral pH. As a result, glargine insulin forms subcutaneous depots after injection, which slowly release insulin into the bloodstream over a period of 24 hours.
Glargine insulin binds to the insulin receptor, which is a tyrosine kinase receptor. This binding activates the insulin receptor, which in turn phosphorylates insulin receptor substrates (IRS). IRS proteins then activate downstream signaling pathways that lead to the uptake of glucose into cells and the inhibition of glucose production by the liver.
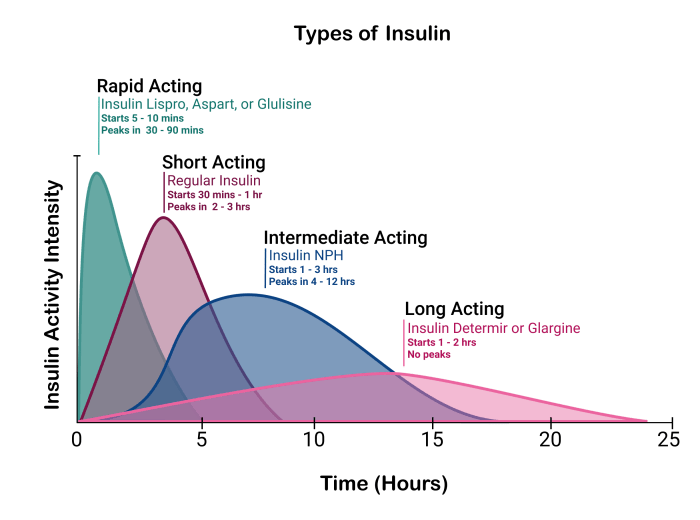
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Onset of action | 2-4 hours |
| Peak action | 8-12 hours |
| Duration of action | 24 hours |
Clinical Applications of Glargine Insulin
Glargine insulin is indicated for the treatment of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. It can be used as a once-daily injection or as multiple daily injections. Glargine insulin is often used in combination with other antidiabetic medications, such as oral agents and GLP-1 agonists.
The dosing of glargine insulin is individualized based on the patient’s blood glucose levels and response to therapy. The starting dose is typically 10 units per day, which can be increased or decreased as needed.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Glargine Insulin
Glargine insulin has several advantages over other types of insulin, including its long duration of action, reduced risk of hypoglycemia, and flexibility in dosing. However, glargine insulin can also cause weight gain, fluid retention, and lipodystrophy.
- Advantages
- Long duration of action (24 hours)
- Reduced risk of hypoglycemia
- Flexibility in dosing
- Disadvantages
- Weight gain
- Fluid retention
- Lipodystrophy
Overall, glargine insulin is a safe and effective treatment for diabetes. It is important to discuss the benefits and risks of glargine insulin with your doctor before starting therapy.
Special Considerations for Using Glargine Insulin: Which Statement Is Correct Regarding Glargine Insulin
There are several special considerations for using glargine insulin in specific populations, such as children, pregnant women, and the elderly. Children and pregnant women may require lower doses of glargine insulin than adults. The elderly may be more susceptible to the side effects of glargine insulin, such as weight gain and fluid retention.
Glargine insulin can interact with several other medications, including oral anticoagulants, beta-blockers, and corticosteroids. It is important to tell your doctor about all of the medications you are taking before starting glargine insulin therapy.
It is important to monitor your blood glucose levels closely while using glargine insulin. You should check your blood glucose levels at least once a day, and more often if you are experiencing symptoms of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. You should also keep a record of your blood glucose levels so that you can discuss them with your doctor at your next appointment.
Question Bank
What is the mechanism of action of glargine insulin?
Glargine insulin binds to insulin receptors on cells, mimicking the action of endogenous insulin. This binding triggers a cascade of intracellular events, leading to increased glucose uptake and utilization by cells, thereby lowering blood glucose levels.
What are the advantages of using glargine insulin?
Glargine insulin offers several advantages, including its long duration of action, reduced risk of hypoglycemia, and flexibility in dosing. It provides a steady, basal level of insulin, making it suitable for once-daily or twice-daily administration.
What are the disadvantages of using glargine insulin?
Potential disadvantages of glargine insulin include weight gain, fluid retention, and lipodystrophy. It is essential to monitor these side effects and adjust the dosage or regimen as needed.