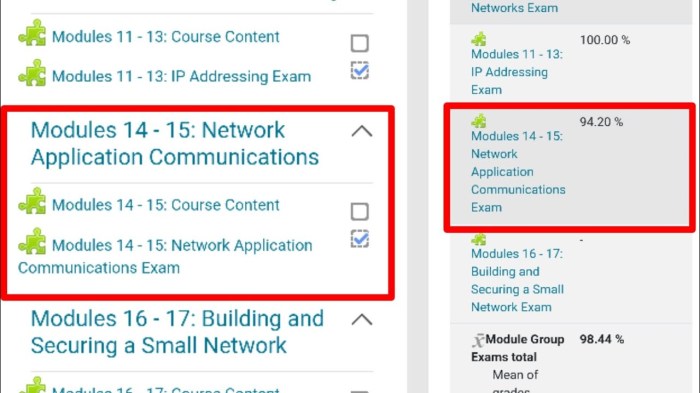
Modules 14 – 15: network application communications exam – Modules 14-15: Network Application Communications Exam delves into the intricacies of network communication, providing a comprehensive understanding of the protocols, standards, and technologies that underpin the exchange of data across networks. This in-depth examination sets the stage for a journey into the fundamentals of network application communications, offering a thorough exploration of the underlying concepts and their practical applications.
From the foundational principles of protocols and standards to the specific roles of application, transport, network, and data link layer protocols, this examination covers a wide spectrum of topics. It delves into the advantages and disadvantages of different protocols, highlighting their suitability for various network applications.
Additionally, it explores the significance of network security and management, emphasizing the importance of safeguarding network communications and ensuring their efficient operation.
Protocols and Standards: Modules 14 – 15: Network Application Communications Exam

Network application communications rely on protocols and standards to establish a common language and ensure interoperability between different devices and applications. Protocols define the rules and procedures for exchanging data, while standards ensure that these protocols are implemented consistently.
Application Layer Protocols
Application layer protocols operate at the highest level of the network stack and are responsible for providing application-specific functionality. Common protocols include:
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): Used for web browsing and file transfer.
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): Used for sending and receiving email.
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol): Used for transferring files between computers.
Transport Layer Protocols
Transport layer protocols provide reliable and efficient data transfer between hosts. The two main protocols are:
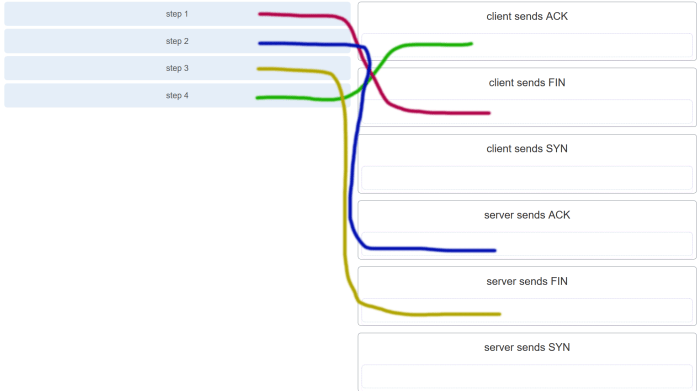
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): Provides reliable, ordered, and error-corrected data delivery.
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol): Provides unreliable, unordered, and fast data delivery.
Network Layer Protocols
Network layer protocols handle the routing and addressing of data packets across the network. Common protocols include:
- IP (Internet Protocol): Defines the addressing scheme and routing mechanisms used on the internet.
- ARP (Address Resolution Protocol): Resolves IP addresses to physical addresses.
Data Link Layer Protocols
Data link layer protocols manage the physical transmission of data over a network medium. Common protocols include:
- Ethernet: A widely used wired network protocol.
- Wi-Fi: A wireless network protocol.
Security in Network Communications
Network communications are vulnerable to various security threats, including eavesdropping, data tampering, and denial of service attacks. To address these threats, various security measures are employed, such as:
- Encryption: Protects data from unauthorized access.
- Firewalls: Blocks unauthorized access to networks.
Network Management, Modules 14 – 15: network application communications exam
Network management involves monitoring, maintaining, and troubleshooting network infrastructure. Key tasks include:
- Performance monitoring: Tracking network performance and identifying bottlenecks.
- Fault management: Detecting and resolving network issues.
Quick FAQs
What are the key protocols used in network application communications?
TCP, UDP, HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SMTP, and DNS are among the most commonly used protocols in network application communications.
What is the role of standards in network communication?
Standards ensure interoperability between different network devices and applications by defining common protocols, data formats, and communication procedures.
What are the advantages of using TCP over UDP?
TCP provides reliable, ordered, and error-checked data transmission, making it suitable for applications that require high data integrity, such as file transfers and web browsing.