Identify the true and false statements about herbert blumer – Embark on a journey into the realm of Herbert Blumer’s groundbreaking contributions to sociology, where we uncover the truths and dispel the falsehoods surrounding his influential theories. As we unravel the enigmatic tapestry of his life and work, we will illuminate the profound impact of his ideas on the discipline.
Blumer, the visionary behind symbolic interactionism, challenged conventional sociological perspectives, emphasizing the significance of human interaction and the construction of meaning in shaping social reality. His legacy continues to inspire contemporary sociological research, leaving an indelible mark on our understanding of the human experience.
Biography of Herbert Blumer

Herbert Blumer (1900-1987) was an American sociologist and the primary architect of symbolic interactionism, a major sociological theory that emphasizes the role of symbols and interaction in shaping human behavior.
Early Life and Education
Blumer was born in St. Louis, Missouri, on March 7, 1900. He attended the University of Missouri, where he earned a bachelor’s degree in journalism in 1922. He later pursued graduate studies in sociology at the University of Chicago, where he studied under Robert Park and Ernest Burgess.
Academic Career
Blumer joined the faculty of the University of Chicago in 1927. He became a full professor in 1935 and served as chair of the sociology department from 1942 to 1952. Blumer was a prolific writer and researcher, publishing numerous books and articles on symbolic interactionism, social psychology, and methodology.
Timeline of Key Events
- 1900: Born in St. Louis, Missouri
- 1922: Earned a bachelor’s degree in journalism from the University of Missouri
- 1925: Earned a master’s degree in sociology from the University of Chicago
- 1927: Joined the faculty of the University of Chicago
- 1935: Became a full professor at the University of Chicago
- 1942-1952: Served as chair of the sociology department at the University of Chicago
- 1952: Published “Symbolic Interactionism: Perspective and Method”
- 1969: Retired from the University of Chicago
- 1987: Died in Berkeley, California
Symbolic Interactionism Theory
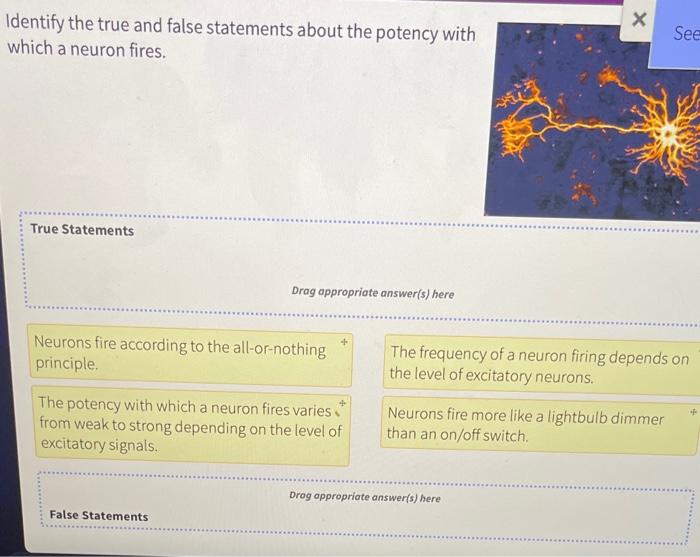
Core Concepts
Symbolic interactionism is a sociological theory that emphasizes the role of symbols and interaction in shaping human behavior. According to Blumer, symbols are anything that represents something else, such as words, gestures, or objects. Interaction is the process by which people communicate and exchange meanings through symbols.
Blumer argued that human behavior is not simply a response to external stimuli, but rather a product of the meanings that people attach to those stimuli. These meanings are developed through interaction with others and are constantly being negotiated and renegotiated.
Differences from Other Sociological Perspectives
Symbolic interactionism differs from other sociological perspectives in several ways. First, it emphasizes the role of the individual actor. Second, it focuses on the process of interaction rather than on social structure. Third, it views human behavior as a creative process rather than a mechanical response to external forces.
Examples of Applications
Symbolic interactionism has been used to study a wide range of social phenomena, including:
- The development of the self
- The formation of social groups
- The process of communication
- The dynamics of social change
Methodological Contributions: Identify The True And False Statements About Herbert Blumer
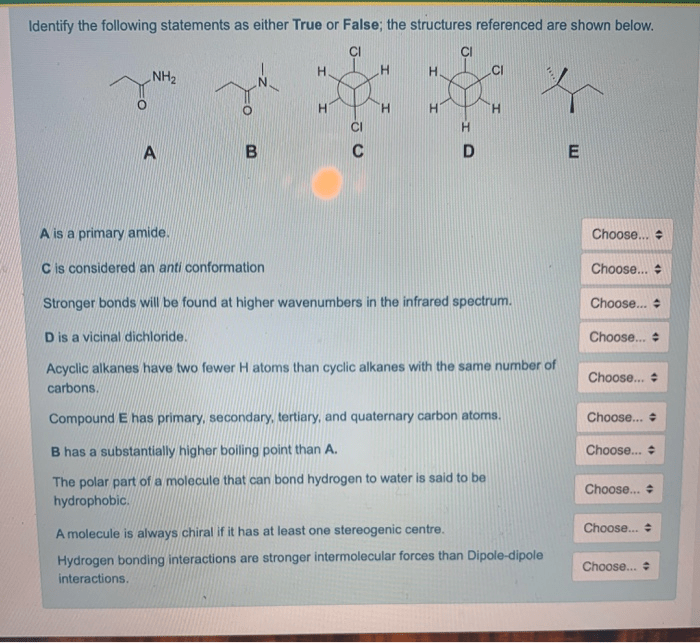
Emphasis on Qualitative Research Methods
Blumer was a strong advocate for qualitative research methods, such as participant observation and interviewing. He argued that these methods allow researchers to gain a deeper understanding of the social world by immersing themselves in the lives of their subjects.
Participant Observation, Identify the true and false statements about herbert blumer
Participant observation is a research method in which the researcher observes and interacts with people in their natural settings. This method allows researchers to collect data on the everyday lives of people and to gain insights into their thoughts and feelings.
Examples of Applications
Participant observation has been used to study a wide range of social phenomena, including:
- The culture of gangs
- The socialization of children
- The dynamics of workplace interactions
- The process of social change
Legacy and Impact

Influence on the Field of Sociology
Blumer’s work has had a profound influence on the field of sociology. Symbolic interactionism is now one of the most widely used sociological theories, and it has been used to study a wide range of social phenomena.
Contemporary Sociological Research
Symbolic interactionism continues to shape contemporary sociological research. It is used to study a wide range of social issues, including:
- The impact of social media on relationships
- The dynamics of race and ethnicity
- The process of globalization
- The challenges of social inequality
Essential FAQs
Was Herbert Blumer the founder of symbolic interactionism?
False. While Blumer is considered one of the most influential proponents of symbolic interactionism, the theory was originally developed by George Herbert Mead.
Did Blumer believe that social reality is objective and external to individuals?
False. Blumer argued that social reality is subjective and constructed through social interaction and the interpretation of symbols.
Is participant observation the only research method advocated by Blumer?
False. While Blumer emphasized the importance of participant observation, he also recognized the value of other qualitative methods, such as interviewing and document analysis.